When you notice that your toenails are discolored and brittle, you might be suffering from toenail fungus. If you are, read on to learn about different types of toenail fungus and how they are treated. In this article, you will learn about the common forms of toenail fungus, including Distal subungual infections, Candidal onychomycosis, and Athlete's foot.
Candidal onychomycosis
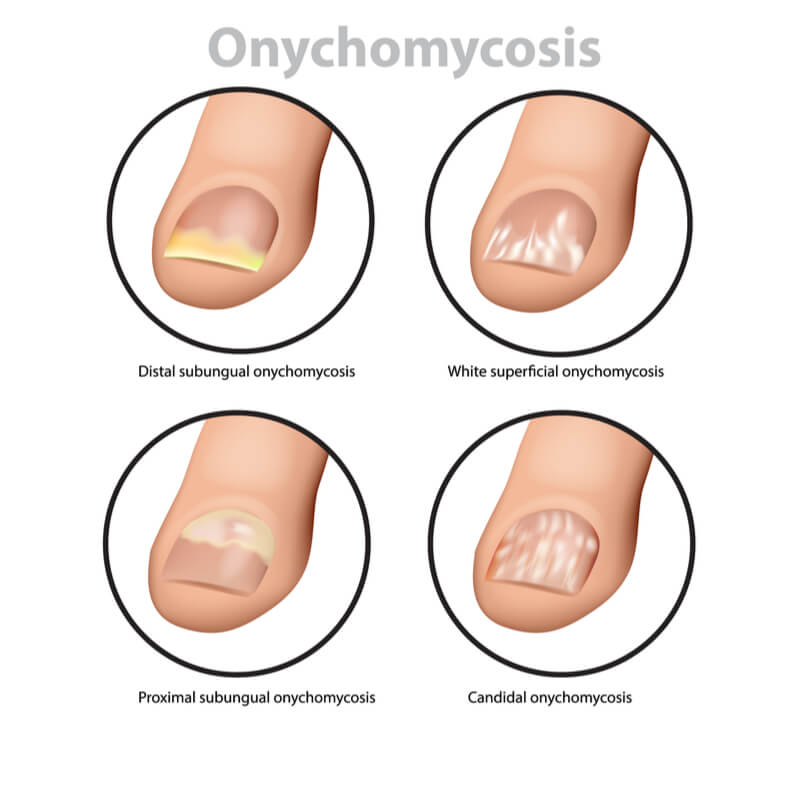
Onychomycosis, or fungal nail infection, is a common disorder of the nails. The condition affects all parts of the nail, including the matrix, nail bed, and nail plate. Symptoms of this infection can range from mild discomfort to painful infections and disfigurement. In severe cases, it can impair one's daily activities, lead to severe physical limitations, and diminish a person's quality of life.
While there is no known cure for onychomycosis, prevention is the best defense against it. Changing socks regularly, wearing shoes that breathe, and trimming nails to a short length are important measures to help prevent fungus. If you experience symptoms of onychomycosis, visit a physician for a proper diagnosis. For prevention, you should avoid sharing personal items with others, such as towels, bathrobes, and socks.
Treatment for onychomycosis includes oral antifungal medications, topical terbinafine, or surgical removal. Treatment depends on the severity of the infection, risk factors, and patient preference. For severe cases, nail removal may be necessary. However, there are other, less effective treatments that can also result in disfigurement. Toenail fungus is more severe than any other fungal infection.
There are two main forms of toenail fungus. Proximal subungual onychomycosis is an uncommon form of infection that starts with white patches on the nail bed near the cuticle. If untreated, the infected nail may even separate from the nail bed. In severe cases, the condition may result in social and psychological problems.
Proximal subungual infection is uncommon, but a highly contagious form of toenail fungus. It starts as a small injury or infection and spreads to the entire nail. Proximal subungual infection is caused by Candida yeasts and affects the fingernail and toenail. People who frequently soak their hands in water are at high risk of contracting this infection.
If you think your toenail fungus is more serious, consider oral antifungal therapy. While topical medications are generally less effective, oral antifungal medications have higher cure rates than topical treatments. However, oral antifungal medications take about nine to twelve months to work. Generally, the most effective medication for onychomycosis and toenail fungus is a combination of topical and oral antifungal agents.
Proximal subungual onychomycosis (PSON) is the least common form of fungal nail infection. It starts at the cuticle and spreads slowly to the nail tip. While T. rubrum is the most common cause of proximal subungual onychomycosis, it is rare in distal subungual toenail fungus.
Besides being a painful and unsightly condition, onychomycosis is also associated with a high risk of secondary bacterial infections. Moreover, it can interfere with a person's lifestyle and may affect their occupation. Moreover, it can have a profound effect on their self-esteem and their lives. As a result, many patients feel embarrassed and have lower self-esteem because of their condition.
Athlete's foot
Several preventive measures can help you protect your feet from toenail fungus. For starters, always wash your feet after exercising. Make sure you dry your feet between your toes thoroughly. Also, wear shoes that breathe and wear socks made of synthetic fiber. These will help wick away moisture from your feet, which will prevent the fungi from growing.
Athletes' foot is usually caused by prolonged exposure to moist or warm places. If you're exposed to wet, warm places, or share shoes and towels with others, you're at greater risk of getting athlete's foot. If you're already affected, you may want to consider an antifungal topical treatment for your feet. However, a topical solution is not a good solution for every case.
Your doctor may diagnose an athlete's foot simply by examining your symptoms. He or she may also order a skin test to determine whether or not you've contracted the fungus. A doctor will likely prescribe an antifungal medication or prescribe you a topical cream. In severe cases, your doctor may prescribe you an oral medication or prescribe you a topical solution.
Athletes' feet can affect any part of your feet but is particularly common in feet where sweat and moisture are high. You'll have a red rash between your toes and an itch, sting, or burn. These symptoms are caused by fungi known as dermatophytes. It spreads by direct contact with moist surfaces, including tight-fitting shoes.
The athlete's foot is the most common type of toenail fungus and can be triggered by sweaty feet. It can also occur due to psoriasis, infection, or an improper footwear choice. Fungal infections on toenails are contagious, so it is important to protect yourself from spreading the fungus.
Fungal infections on the nails can occur at any age but are more common among elderly people. Aging nails tend to become brittle and dry, and cracks in the nails can allow fungi to grow. Furthermore, people with poor immune systems are more likely to contract toenail fungus than healthy individuals. Fungal infections may also lead to odor, thickening, or brittle nails. Luckily, treatments are available for toenail fungus.
To treat onychomycosis, doctors must first diagnose it. Onychomycosis, also known as athlete's foot, is characterized by white spots on the nail's surface. The infection can spread to the rest of the nail and may even spread to the mucus membranes. Treatment will depend on the type of infection. Toenail fungus can be cured with prescription medications.
Treatment for toenail fungus is often a combination of topical creams and oral antifungal drugs. Topical treatments are more effective for toenail fungus, but oral medications can cause severe side effects such as liver damage and allergic reactions. A doctor's diagnosis is necessary because toenail fungus is difficult to treat, often taking months to clear.
Distal subungual infections
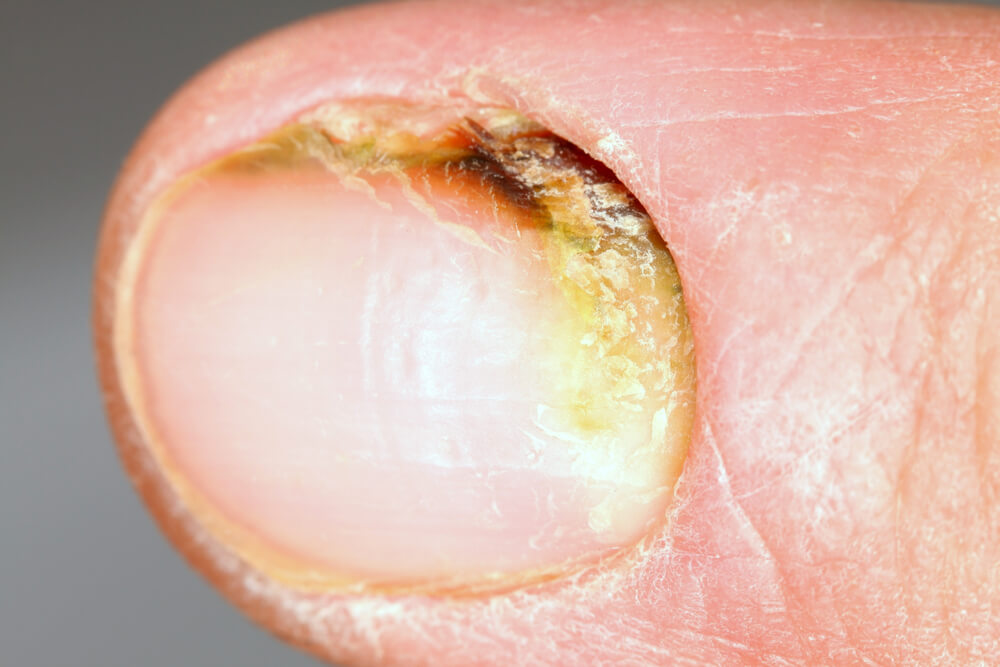
The most common type of toenail fungus is distal subungual onychomycosis. This condition causes a yellow spot to appear on the base of the nail. The infection continues upward and can cause the nail to become thickened and flaky. Proximal subungual infections occur when a person suffers from an injury to their nail. Candida yeasts cause proximal subungual infections. Those who often soak their hands or feet are at a greater risk of this infection.
Treatment for distal subungual infections in toenails depends on the type of fungus. Some doctors may recommend an antifungal ointment. However, these solutions may not completely clear the body of the infection. A fungal infection may lead to further complications. In addition to treatment options, lifestyle changes may be necessary to prevent future infection of the nails. Toenail care should include clipping, filing, and trimming of nails to prevent fungus from spreading and keeping the surrounding skin healthy. Wear rubber gloves when cleaning the area.
There are three types of toenail fungus. Athlete's Foot is the most common type, accounting for about 50% of consultations related to nail disorders. Infections of the toenails tend to spread deeper, resulting in a weak nail that can fall off. Another type is called white superficial onychomycosis, which affects the entire nail.
When treating distal subungual infections in toenails, it is important to follow the proper procedures to remove and dispose of the infection. The nail bed must be cleaned with alcohol before it is examined. A nail bed sample should be taken from the underlying nail bed close to the lunula and the cuticle. Occasionally, the surface of the nail can be removed for examination.
If you're experiencing symptoms of toenail fungus, oral antifungal therapy is the best option. It has a high cure rate but can take nine to 12 months to take effect. It's shorter than topical therapy, but the risk of side effects is higher. Griseofulvin has been the mainstay of oral antifungal therapy for decades but has recently been replaced by newer agents.
Topical antifungals can be used in a variety of ways. Among these are terbinafine and butenafine. These are both effective in killing fungi and killing some pathogens. Terbinafine has the highest risk of side effects and is usually reserved for people with more severe or resistant forms of the condition. While there are some medications that are not FDA-approved for toenail fungus, topical agents are a more affordable option.


Comments
Loading…