Table of Contents
Diabetics and seniors should think when eating
Grapefruits are known for their refreshing taste and numerous health benefits. However, for certain individuals, such as diabetics and seniors, consuming grapefruits may require extra caution. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the factors that make grapefruits potentially problematic for these specific groups. We will delve into the effects of grapefruits on blood sugar levels, medication interactions, and potential risks for seniors. By understanding these considerations, individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating grapefruits into their diet.

The Impact of Grapefruits on Blood Sugar Levels
Grapefruits, renowned for their high vitamin C content and fiber, are often regarded as a healthy choice. However, individuals with diabetes need to be mindful of their effects on blood sugar levels. Here's a detailed breakdown of the key considerations:
Glycemic Index (GI) of Grapefruits
Grapefruits have a low glycemic index, typically ranging from 25 to 45. This low GI indicates that grapefruits have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. The presence of fiber, including both soluble and insoluble fiber, helps to slow down the absorption of sugars in the bloodstream.
Fiber Content
Grapefruits are an excellent source of dietary fiber. This fiber content assists in regulating blood sugar levels by slowing down the release of sugars into the bloodstream. The soluble fiber present in grapefruits forms a gel-like substance, which aids in controlling blood sugar spikes after a meal.
Natural Sugar Content
While grapefruits contain natural sugars, including fructose, their overall sugar content is relatively low compared to other fruits. However, it is important to note that consuming large quantities of grapefruit can still cause a notable increase in blood sugar levels.
Individual Responses
Every individual's body reacts differently to foods, including grapefruits. Factors such as insulin sensitivity, overall diet, and physical activity levels can influence the body's response to grapefruit consumption. It is essential for individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels closely and consult with their healthcare provider to determine the ideal portion sizes and frequency of grapefruit consumption.
Meal Planning and Portion Control:
Incorporating grapefruits into a well-balanced meal plan is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Pairing grapefruits with protein and healthy fats can further slow down the digestion and absorption of sugars, resulting in a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream. Practicing portion control and monitoring blood sugar levels can help individuals manage their diabetes effectively.
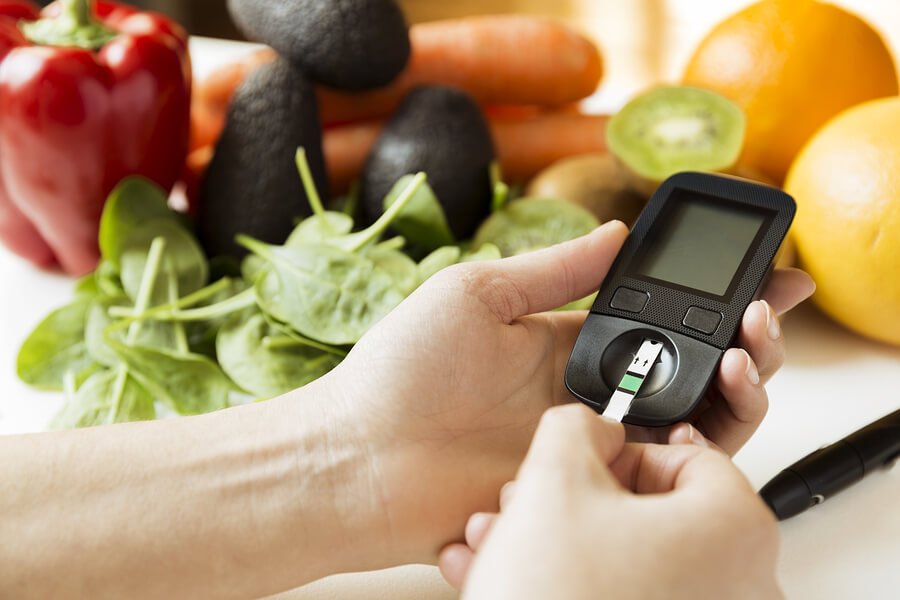

Medication Interactions with Grapefruits
Grapefruits have gained attention for their potential to interact with specific medications, which can pose risks and impact treatment outcomes. Understanding these interactions is crucial for individuals who are prescribed certain drugs. Here's an in-depth exploration of the topic:
Grapefruit and Cytochrome P450 Enzyme
Grapefruits contain compounds known as furanocoumarins that inhibit the activity of the enzyme cytochrome P450 in the liver. This enzyme plays a vital role in metabolizing various medications. When grapefruit interferes with this enzyme, it can disrupt the normal breakdown and elimination of certain drugs from the body. As a result, the concentration of these drugs in the bloodstream may increase, leading to potential side effects or reduced efficacy.
Medications Affected by Grapefruit
Several classes of medications are known to interact with grapefruit. These include:
- Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs: Grapefruit can interact with statins, a common class of cholesterol-lowering medications. The interaction can result in increased blood levels of the drug, potentially increasing the risk of side effects such as muscle pain and liver damage.
- Blood Pressure Medications: Some calcium channel blockers, a type of blood pressure medication, can be affected by grapefruit. The interaction can lead to higher levels of the drug in the bloodstream, potentially causing an excessive drop in blood pressure or other adverse effects.
- Immunosuppressants: Grapefruit can interfere with certain immunosuppressant drugs, which are often prescribed to individuals who have undergone organ transplants. Interaction with grapefruit can alter the blood levels of these medications, affecting their effectiveness in preventing organ rejection.
- Psychiatric Medications: Grapefruit can also interact with certain psychiatric medications, including some antidepressants and antipsychotics. The interaction can increase the drug's concentration in the blood, potentially leading to an intensified sedative effect or other adverse reactions.
Importance of Healthcare Provider Consultation
If you are taking any of the medications mentioned above or others that may interact with grapefruit, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider. They can provide specific guidance based on your individual medication regimen and health condition. Your healthcare provider may recommend alternative medications, adjust the dosage, or advise against grapefruit consumption altogether to ensure the safety and effectiveness of your treatment.

Considerations for Seniors
Seniors have unique health concerns that require special attention when it comes to grapefruit consumption. Let's delve into the specific factors to consider:
Medication Regimens of Seniors
Seniors often have multiple health conditions and may be managing several medications. It is crucial to be aware that grapefruits can interact with certain drugs, potentially leading to adverse effects. The interaction occurs because grapefruits contain compounds that inhibit enzymes responsible for metabolizing medications in the liver. This inhibition can result in higher drug concentrations in the bloodstream, increasing the risk of side effects or reducing the medication's effectiveness.
To ensure the safe use of medications, seniors should consult their healthcare provider before consuming grapefruits. By discussing their medication regimens, potential risks, and necessary adjustments, healthcare providers can guide seniors on whether grapefruit consumption is suitable or if alternatives should be considered.
Nutrient Requirements for Seniors
Seniors have specific nutrient requirements to support their overall well-being. Grapefruits can be a valuable addition to their diet as they are rich in essential nutrients. Here are some key benefits of grapefruit consumption for seniors:
- Vitamin C: Grapefruits are an excellent source of vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that plays a vital role in immune function. Adequate vitamin C intake can help seniors maintain a healthy immune system, which becomes increasingly important with age. Additionally, vitamin C aids in collagen production, contributing to healthy skin and supporting wound healing. Furthermore, vitamin C enhances iron absorption, which is important for preventing anemia.
- Fiber: Grapefruits are a good source of dietary fiber. The fiber found in grapefruits, both soluble and insoluble, offers several benefits for seniors. It promotes healthy digestion by supporting regular bowel movements, preventing constipation, and reducing the risk of digestive disorders. Additionally, dietary fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels, aids in maintaining a healthy weight, and supports heart health by reducing cholesterol levels.
- Antioxidants: Grapefruits contain a variety of antioxidants, including flavonoids and vitamin C. Antioxidants play a crucial role in protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can lead to oxidative stress and contribute to various chronic diseases. By including grapefruits in their diet, seniors can benefit from the antioxidant properties of these fruits, supporting overall well-being and potentially reducing the risk of age-related health issues.
However, it is important to note that while grapefruits offer significant health benefits, moderation and consideration of individual health conditions and medication interactions are essential. Seniors should work closely with their healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate portion sizes, frequency of consumption, and any necessary modifications based on their specific health needs.

Moderation and Portion Control
Grapefruits can provide health benefits, but it is essential to consume them in moderation, especially for diabetics and seniors. Moderation helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of potential adverse effects. To ensure responsible consumption, here are some detailed tips for practicing portion control when enjoying grapefruits:
Choose Smaller-Sized Grapefruits
Opt for smaller-sized grapefruits to manage portion sizes effectively. These smaller fruits still provide the same nutritional benefits but with reduced sugar content. Selecting smaller grapefruits allows for better control over carbohydrate intake, which is particularly crucial for individuals with diabetes.
Divide Larger Grapefruits
If you have a large grapefruit, consider dividing it into smaller servings. Cut the grapefruit into sections or slices and store the remaining portions in the refrigerator for later consumption. This approach helps control the amount of grapefruit consumed in a single sitting, making it easier to manage blood sugar levels and prevent excessive sugar intake.
Pair Grapefruit with Other Nutritious Foods
Incorporate grapefruit as part of a balanced meal or snack by combining it with other nutritious foods. For example, enjoy a serving of grapefruit alongside a source of lean protein, such as Greek yogurt or cottage cheese. This pairing helps slow down the digestion of sugars and provides a more balanced nutrient profile. Adding a source of healthy fats, like nuts or seeds, can further enhance the nutritional value and promote satiety.
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
It is crucial for individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, especially after consuming grapefruit or any other food that may impact blood sugar. This practice allows for better understanding of individual responses to grapefruit consumption and helps in adjusting medication, if necessary.
Other Considerations for Diabetics
When it comes to grapefruit consumption, there are additional considerations for individuals with diabetes. Here are some detailed points to keep in mind:
Individual Blood Sugar Responses
Each individual may have a unique response to consuming grapefruits, even among those with diabetes. Some individuals may experience significant fluctuations in blood sugar levels after consuming grapefruits, while others may have a more stable response. Factors such as insulin sensitivity, overall diet, physical activity levels, and medication use can all influence individual blood sugar responses.
To better understand how grapefruits affect blood sugar levels, it is important for individuals with diabetes to regularly monitor their blood glucose levels. This practice can provide valuable insights into how their body responds to grapefruit consumption and help in making appropriate adjustments to their diabetes management plan. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can offer further guidance on managing blood sugar levels effectively.
Pairing Grapefruits with Protein or Fiber
To mitigate the potential impact of grapefruits on blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can consider pairing them with protein or fiber-rich foods. Protein and fiber both contribute to slower digestion and absorption of sugars, which can help maintain more stable blood sugar levels. Here are some examples of protein and fiber-rich options that can be paired with grapefruits:
- Greek Yogurt: Enjoying grapefruit with a serving of Greek yogurt provides protein, calcium, and probiotics, offering a well-rounded and satisfying snack.
- Nuts and Seeds: Adding a handful of nuts or seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, or chia seeds, to your grapefruit can provide a good source of healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
- Nut Butter: Spreading a tablespoon of almond butter or peanut butter on grapefruit slices can provide additional protein and healthy fats, which help slow down sugar absorption.
Section 6: Alternatives and Modifications for Seniors
Seniors may need to explore alternative options or modifications when it comes to grapefruit consumption. Here are some detailed considerations:
Alternative Citrus Fruits
If seniors are advised to avoid grapefruits due to medication interactions or specific health concerns, there are several alternative citrus fruits that can provide similar nutritional benefits. These fruits offer vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants without posing the same potential risks as grapefruits. Here are some citrus fruits to consider:
- Oranges: Oranges are a popular citrus fruit known for their sweet and juicy flavor. They are an excellent source of vitamin C and provide dietary fiber, promoting a healthy immune system and digestive function.
- Tangerines: Tangerines are smaller citrus fruits that are easy to peel and have a slightly sweeter taste compared to oranges. They are also rich in vitamin C and fiber, making them a great alternative to grapefruits.
- Lemons: Lemons have a tangy and refreshing flavor, and they are well-known for their high vitamin C content. While they are less sweet than grapefruits, lemons can still add a burst of citrus flavor to dishes and beverages.
- Limes: Limes offers a zesty and sour taste, packed with vitamin C and antioxidants. They can be used in cooking, baking, or as a flavor enhancer in beverages.
These alternative citrus fruits provide a range of health benefits similar to grapefruits, allowing seniors to enjoy the nutritional advantages without the potential risks.
Juicing and Blending Modifications
For seniors who have difficulty consuming whole grapefruits, modifications such as juicing or blending can be considered. These modifications can help make the fruit more easily consumable while still retaining its nutritional value. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making any modifications, especially if there are concerns about medication interactions or blood sugar management. Here are some important points to keep in mind:
- Juicing: Juicing grapefruits can be an option for seniors who struggle with chewing or swallowing. Freshly squeezed grapefruit juice can be consumed in smaller portions to manage sugar intake. It is essential to monitor blood sugar levels and consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that the juice is compatible with medication regimens.
- Blending: Blending grapefruits, including pulp and fiber, into smoothies can provide a convenient and nutritious option for seniors. Blended grapefruit can be combined with other fruits, vegetables, and protein sources to create well-rounded and balanced smoothies. However, it is important to monitor portion sizes and consider the overall carbohydrate content to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
While grapefruits offer a range of health benefits, it is crucial for diabetics and seniors to approach their consumption with caution. The impact on blood sugar levels and the potential medication interactions associated with grapefruit consumption should not be overlooked. Consulting with healthcare professionals and closely monitoring individual responses can help individuals make informed decisions about including grapefruits in their diet.
Remember, every individual is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. By prioritizing personal health needs, considering individual responses, and seeking professional guidance, individuals can navigate the complexities and enjoy the potential benefits of grapefruit consumption safely.



Comments
Loading…