If you suffer from back pain or leg pain, you may be wondering whether surgery can help you. This article will discuss the causes of sciatica and the treatments available for the condition. You may also want to read more about the various causes of sciatica and why surgery is sometimes the best option. The following paragraphs will discuss both types of surgery. The most common surgeries for sciatica are spinal fusions and lumbar fusions.
Treatment options for sciatica

Conservative treatments for bilateral sciatica may include applying heat or cold packs to the affected area or other treatments, including physical therapy. Your doctor may perform diagnostic imaging, such as MRI and discograms, to determine the cause of sciatica. In some cases, spinal decompression surgery may be recommended to restore full function. Conservative therapies should be attempted first before undergoing invasive procedures. NSAIDs and acetaminophen may help reduce symptoms.
Chiropractic care is another option for pain relief. Chiropractic adjustments may improve the alignment of the spine, thereby relieving pain. Manual massage can also be effective in managing symptoms. Acupuncture treatments may also be beneficial. Physical therapy also involves adjusting the patient's posture and performing various exercises. Moreover, acupuncture is also beneficial for addressing pain. However, acupuncture and chiropractic adjustments should be performed by trained health professionals.
Surgery is an option for patients who are unable to tolerate non-surgical treatments. Some people may benefit from surgery, but the risks are higher than those associated with nonsurgical treatments. In many cases, the patient may develop nerve damage if nonsurgical treatments do not relieve the symptoms. Left untreated, sciatica symptoms can become permanent. While surgery is an effective treatment option for many, it is not appropriate for everyone with bilateral sciatica.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are a common first-line treatment for sciatica. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) reduce inflammation, and muscle relaxants such as naproxen and acetaminophen can help patients recover from pain. Corticosteroids and other steroid injections are sometimes used to treat severe cases of sciatica. However, these treatments are expensive and often have negative side effects.
While conventional drugs can relieve sciatica pain, newer treatments are more effective than ever. Non-opioids and habit-forming pain relievers, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can be used to treat the condition. Several drugs can be used in combination to control severe pain and treat sleep issues. For those with a high risk of addiction, corticosteroid injections may be necessary.
Causes
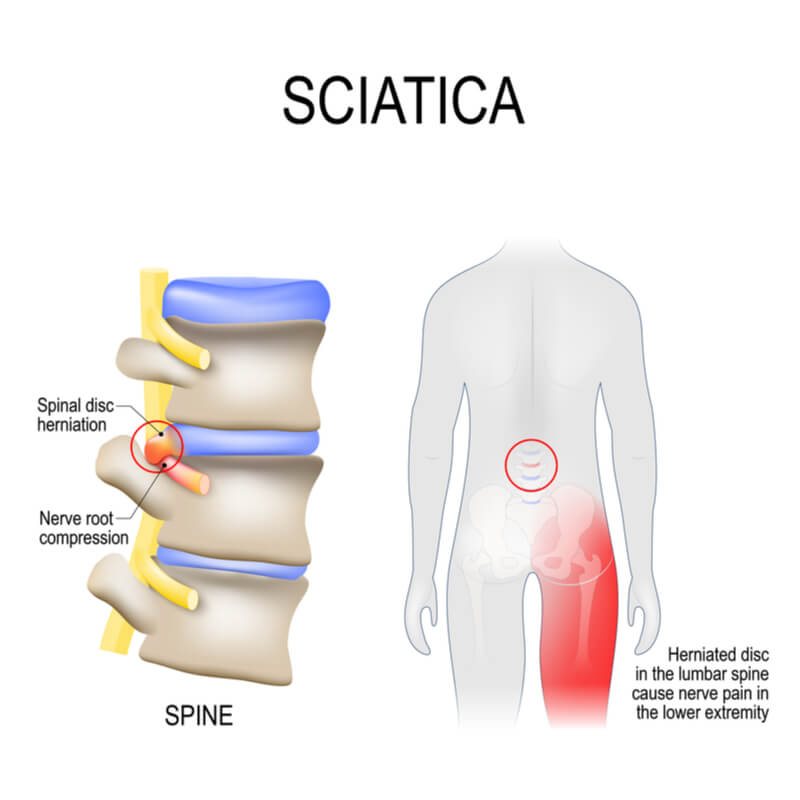
The symptoms of sciatica can vary from patient to patient. Some patients experience consistent symptoms over a long period of time, while others experience unpredictable recurrences. Regardless of severity, it is important to document your symptoms for your doctor's benefit. Detailed documentation will help you distinguish between spinally motivated sciatica and pseudo sciatica. Listed below are some of the most common causes of bilateral sciatica.
Regardless of the cause, it's essential to get plenty of sleep. A healthy amount of sleep allows the body to repair the damage. A good night's sleep also helps the body recover from an injury or illness. While you're at it, read up on the most common symptoms of sciatica. You'll be glad you did. And, don't forget to ask your doctor for advice. Sciatica is a common condition, and the symptoms can affect your everyday life.
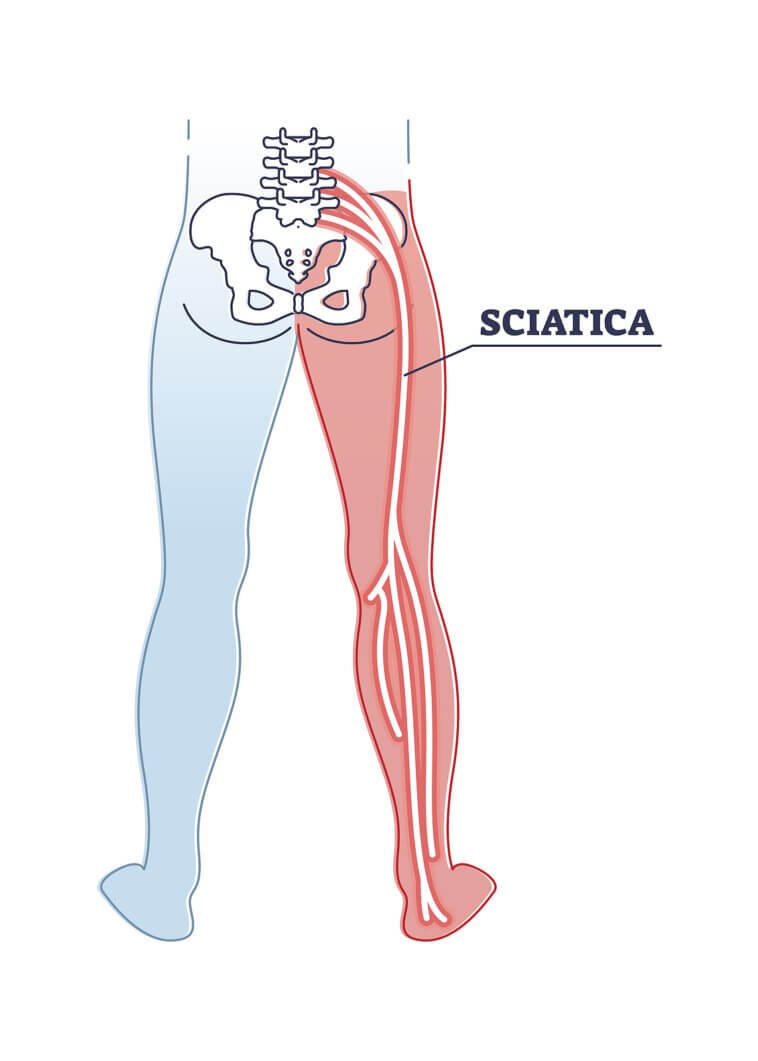
For patients with bilateral sciatica, the primary suffering from this condition is pain. The pain typically radiates down one leg and is described as burning or numbness. Lie down to ease the symptoms. X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and electromyography may be ordered to determine the source of the pain. If none of these tests reveal a problem, your doctor may recommend a spinal fusion.
When the pain persists, it's time to seek medical attention. If the pain doesn't vary when you exert yourself, your problem is serious. In fact, the pain may get worse without physical exertion. This is a warning sign of an underlying problem. If you're not seeing any improvement within the next few weeks, you should seek medical attention. And remember to exercise properly. You'll need the strength and stability of your core muscles to keep your back healthy.
Other causes of bilateral sciatica include spinal stenosis and a herniated disc. Inflammation or degeneration of the spine can also cause compression of the sciatic nerve. Although this pain is typically only felt on one side, it can be sporadic. The sciatic nerve is located in the lumbar region of the spinal cord and runs the length of both legs. Symptoms of bilateral sciatica are a warning sign of more serious conditions.
Treatment options
There are a variety of treatment options for patients with sciatica. The initial step in treating this condition is to determine the cause. An MRI or discogram can help your doctor determine if sciatic nerve damage is present. Once a diagnosis has been made, the doctor will determine the appropriate course of treatment. Treatment for this condition may involve surgery, or other options, depending on the severity of the pain and its underlying cause. The goal of treatment for sciatica should be to provide long-term pain relief.
Physical therapy can help people with sciatica to reduce pain and inflammation and resolve the compression. It also allows patients to move without discomfort. During the early stages of the condition, physicians may recommend bed rest. However, it is important to note that bed rest is not a good option. Physical therapy helps patients to strengthen their core muscles and avoid sitting in one position for extended periods. In the case of severe sciatica, steroid injections can help patients get back to their normal activities.
Non-surgical treatment can be an option for patients with mild cases of bilateral sciatica. While non-surgical treatments can be effective for many, more invasive procedures are often necessary for severe cases. Surgical treatment can provide relief from some of the most severe symptoms. The pain associated with sciatica usually responds to non-surgical treatments. If left untreated, surgical treatment may be the best option. Even if conservative treatment is not sufficient, surgery may help you get back on your feet and enjoy a pain-free life.
Surgery is another option for treating symptoms caused by sciatic nerve compression. This procedure is useful if the sciatic nerve is caused by a disc herniation, arthritis, stenosis of the spinal canal, or bone spurs. While these treatments are effective, they are not a permanent solution for sciatica. It is important to seek professional advice about your symptoms because many cases can be treated without surgery.
Surgery
If you are experiencing severe pain, such as that you are unable to function normally, surgery for bilateral sciatica may be a viable option. The surgery involves cutting a portion of the back that presses on the nerve, and it can cost anywhere from twenty to nine thousand dollars. These costs include the surgery, any pre, and post-opp appointments, medication, and additional therapy. Some insurance providers may cover some of these costs.
Patients who have been prescribed pain relievers may also undergo steroid injections or physical therapy. Patients may also opt for nerve blocks. Surgical treatment may also be recommended for individuals with complex cases. While surgery is the last resort in the management of sciatica, it does provide quick relief from pain and tingling sensations. However, you should not immediately choose surgery as the only option. Your doctor will work with you to determine what is best for you.
The causes of sciatica are not understood, but some common causes include multiple level disc herniation, single-level herniation, and central spinal stenosis. The pain is usually mild to moderate in severity and can interfere with everyday activities such as sitting or standing for prolonged periods of time. In severe cases, patients may even experience bowel or bladder problems or weakening of the leg.
In some cases, spinal stenosis or bone spurs may be the cause of sciatica pain. Generally, spinal stenosis narrows the space around the spinal cord, putting pressure on the nerve. In these cases, a surgeon can remove a portion or all of the lamina, which is the roof of the spinal canal. The surgery typically takes one to three hours. Afterward, the patient can walk.
Depending on the severity of sciatica, a doctor may recommend spinal surgery to alleviate symptoms. The surgical procedure performed will depend on the severity of sciatica and its cause. Microdiscectomy is the most common type of spinal surgery for sciatica. The surgeon will also remove the bone spurs that surround the disc. Facetectomy, on the other hand, involves removing the facet joints. In either case, the patient will be able to get back to daily activities soon afterward.


Comments
Loading…